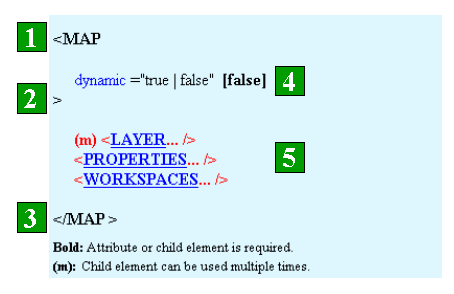
The ArcXML element structure includes the element name, attributes, and child elements. Elements and attributes in ArcXML are case sensitive.
Element Name
- The opening element starts with a less than symbol (<) and is followed by its name. Elements are always written in uppercase letters.
- The opening element ends with a greater than symbol (>).
- The closing element is similar to the opening element. It begins with the less than symbol and a forward slash (/) and is followed by its name. The element ends with a greater than symbol.
- If the element includes any attributes, they are included after the opening element.
- All child elements are inserted before the closing element.
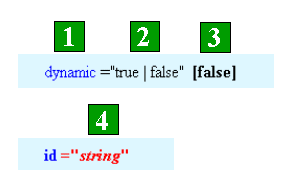
Attributes
- Attributes are always written in lowercase letters. If the attribute is required, it is bold. A definition of each attribute is found in the attribute table for the element.
- If an attribute has a defined list of valid values, all possible values are listed. Only one value can be used at a time. Attribute values are always placed inside double quotes ("), and the text is not case sensitive unless noted. However, if you are using an XML Data Type Definition (DTD) to validate map configuration files, requests, and responses, the text is case sensitive. The enumerated values in the DTD are the same case as defined for each element attribute in this document. In general, most attribute values are all lowercase.
- If the attribute has a default value, it is listed in brackets after the attribute list or type.
- If an attribute does not have a list of known values, the value type is listed such as double, integer, and string.
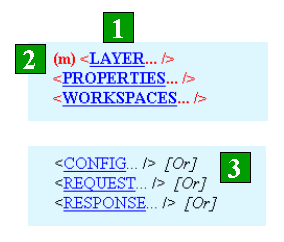
Child Elements
- Child elements are always written in uppercase letters. If the child element is required, it is bold. Each child element is linked to the corresponding page describing that element.
- Some child elements can be used multiple times. If this is the case, the letter "m" in parentheses (m) is in front of the child element.
- In some cases, special instructions are given in brackets after the element. The most common scenario is when a group of child elements is listed but only one child element can be used. In this example, [Or] means to select one child element from the group. More details are given in the Restrictions section to explain special instructions.