Page 10 - Thematic Mapping Excerpt
P. 10
LA County CA
Cook County IL
Proper perspective
Extruded prisms in an axonometric view
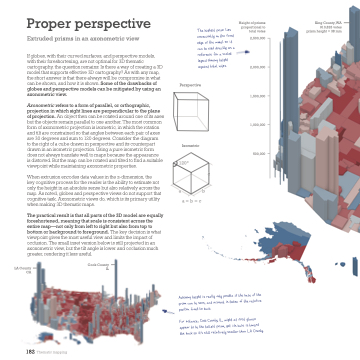
If globes, with their curved surfaces, and perspective models, with their foreshortening, are not optimal for 3D thematic cartography, the question remains: Is there a way of creating a 3D model that supports effective 3D cartography? As with any map, the short answer is that there always will be compromise in what can be shown, and how it is shown. Some of the drawbacks of globes and perspective models can be mitigated by using an axonometric view.
Axonometric refers to a form of parallel, or orthographic, projection in which sight lines are perpendicular to the plane of projection. An object then can be rotated around one of its axes but the objects remain parallel to one another. The most common form of axonometric projection is isometric, in which the rotation and tilt are constrained so that angles between each pair of axes are 30 degrees and sum to 120 degrees. Consider the diagram
to the right of a cube drawn in perspective and its counterpart drawn in an isometric projection. Using a pure isometric form does not always translate well to maps because the appearance
is distorted. But the map can be rotated and tilted to find a suitable viewpoint while maintaining axonometric properties.
When extrusion encodes data values in the z-dimension, the
key cognitive process for the reader is the ability to estimate not only the height in an absolute sense but also relatively across the map. As noted, globes and perspective views do not support that cognitive task. Axonometric views do, which is its primary utility when making 3D thematic maps.
The practical result is that all parts of the 3D model are equally foreshortened, meaning that scale is consistent across the entire map—not only from left to right but also from top to bottom or background to foreground. The key decision is what viewpoint gives the most useful view and limits the impact of occlusion. The small inset version below is still projected in an axonometric view, but the tilt angle is lower and occlusion much greater, rendering it less useful.
Te t pm s y n e ft e f e l o t cn e d iy s a
ee o a cd d g t gt tl s.
Perspective
Height of prisms proportional to
total votes 2,500,000
2,000,000
1,500,000
1,000,000
500,000
King County, WA 910,823 votes prism height = 38 mm
Isometric
120 °
ab a = b =c
c
Ag t s ey y e f e be f e pm cn e , d t s tn f e le n ft o bk.
Fr t, Ck C, IL, t t it le er o e e tt p, t s be s wd e bk o t’s l ly me hn LA Cy.
182 Thematic mapping